Notes on "Introduction to Self-Determination Theory: An approach to motivation, development and wellness"

Week 1 / What is Motivation; Intrinsic Motivation
Three basic psychological needs according to the self-determination theory:
- Autonomy - willingly doing what you're doing; endorse your own actions.
- Competence - feel effective and capable in the activities that you're engaged in.
- Relatedness - feel connected with and belonging in the atmosphere in which you're in.
These are also factors associated with the facilitation of intrinsic motivation.
- Example 1: provide choices -> autonomy -> intrinsic motivation
- Example 2: "If you want your kids to eat vegetable, give them some choices"
Week 1 / Rewards & Intrinsic Motivation
The effect of rewards on free-choice behavior [1]
- Verbal rewards: positive
- Tangible & unexpected rewards: neutral
- Tangible & expected rewards: negative
the undermining effect occurs because the reward shifts the perceived locus of causality. Whereas before I was doing it because I wanted to, now I'm doing it because you've rewarded me and that means that my behavior has become dependent on your rewards and I've lost the intrinsic motivation I already had.
Week 2 / Extrinsic Motivation and the Continuum of Relative Autonomy
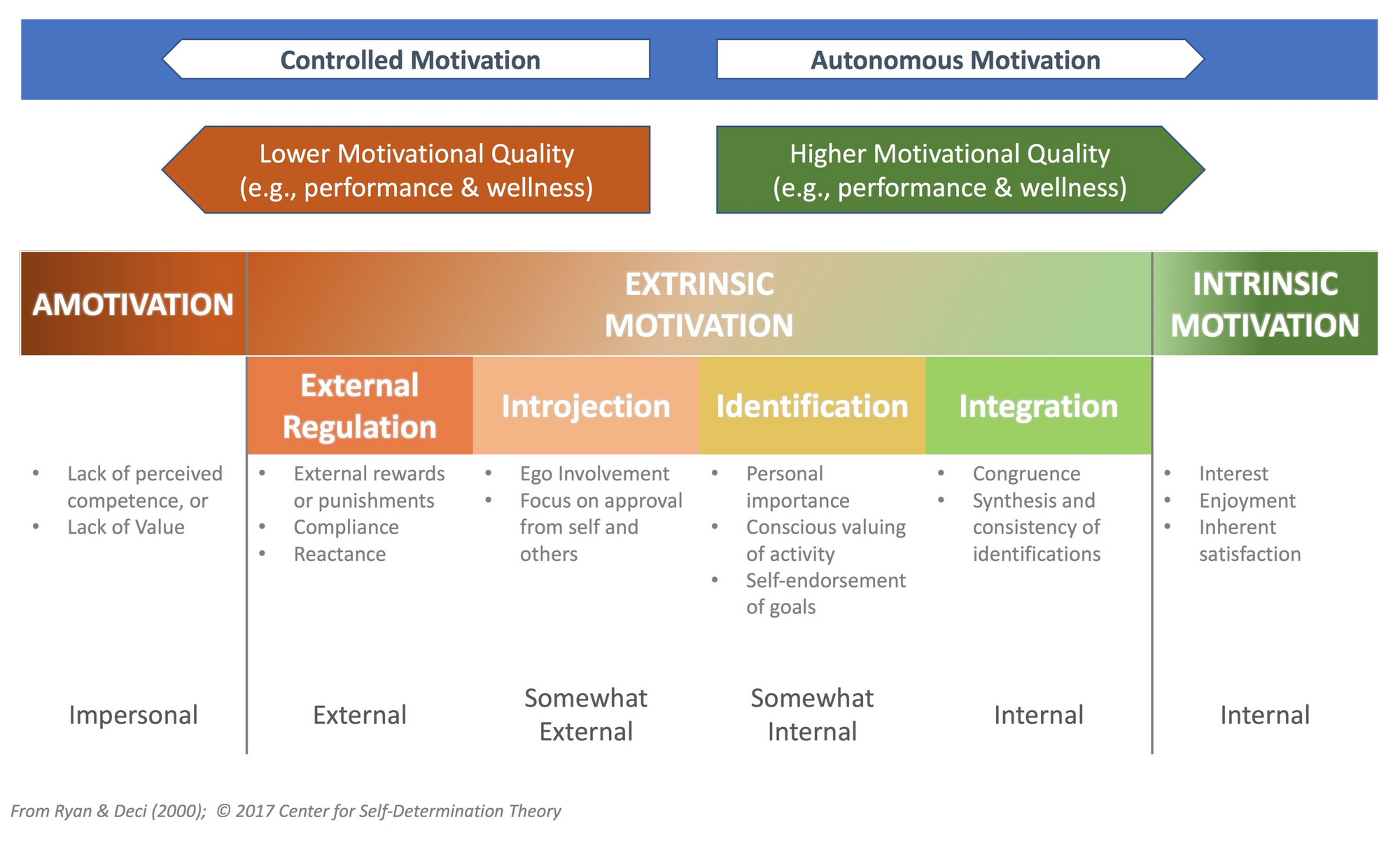
Week 5 / Final Remarks
We have to do things to satisfy our needs
- That often takes proactivity and courage
We can be more...
- Mindful (Open and receptive awareness of what is occurring in the current moment)
- Reflective
- Authentic & Congruent
Reference
[1] Deci, E. L., Koestner, R., & Ryan, R. M. (1999). A meta-analytic review of experiments examining the effects of extrinsic rewards on intrinsic motivation. Psychological Bulletin, 125, 627-668.